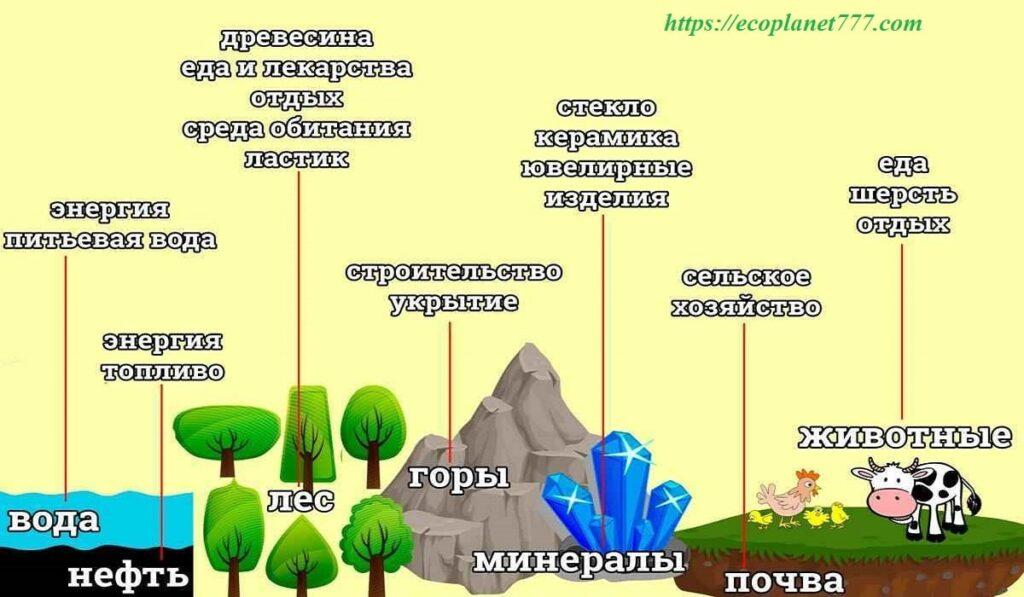
Natural resources are materials created in nature, with their own types and classes, which are used and suitable for human use. These include natural substances (eg soil, water) and energy sources (eg coal, gas) that serve to satisfy human needs and desires.
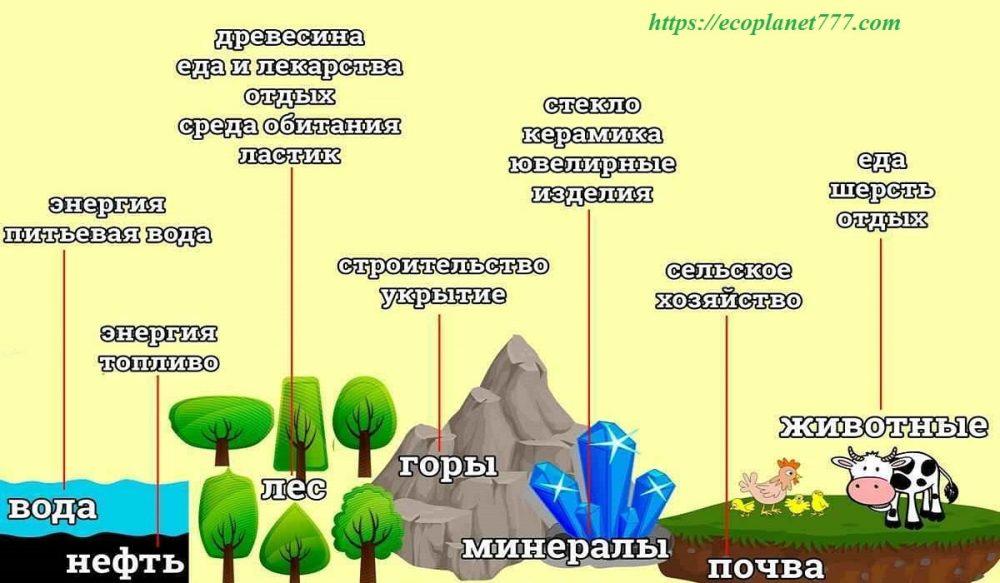
The natural resources of the Earth are vital for the survival and development of mankind. Ultimately, these are the riches provided by nature, from which any benefit can be derived, whether tangible or intangible.
Earth’s natural resources
Natural resources are the materials of the Earth that are used to support life and meet the needs of people. These resources are limited by the Earth’s ability to renew them.
Any natural substance used by humans can be considered a natural resource. Oil, coal, natural gas, metals, stone and sand are natural resources. Other types of natural resources include air, sunlight, soil and water. Animals, birds, fish and plants are also natural resources.
Natural resources are used to produce food, fuel and raw materials, materials for the production of goods.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the Earth’s resources.
Soil
Soil is vital for food production.We need high quality soil to grow the crops we eat and use for our livestock. Soil is also important for plants that grow in the wild.
Poor farming practices deplete the nutrients in the soil.
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variety of living things that inhabit the Earth. The products and benefits we receive from nature depend on biodiversity. We need animals and plants to provide us with food, building materials and medicines, and to keep the landscape clean and healthy.
When a species dies out, it is lost to the world forever. Scientists estimate that the current rate of extinction is 1,000 times the natural rate of renewal. Through hunting, pollution, habitat destruction and global warming, humans are accelerating the loss of biodiversity at an alarming rate.
Fossil fuel
Fossil fuels are fuels derived from the remains of ancient plants and animals. These include coal, petroleum (petroleum), and natural gas. Humans use fossil fuels to power vehicles such as cars and aircraft, to generate electricity, and for cooking and heating.
Also, many of the products we use today are made from petroleum. These include plastics, synthetic rubber, fabrics such as nylon, drugs, cosmetics, wax, cleaning products, medical devices, and even chewing gum.Fossil fuels have been formed over millions of years, stored deep in the earth, and are a non-renewable resource.
We need to conserve fossil fuels so they don’t run out. However, there are other good reasons to limit the use of fossil fuels. These fuels pollute the air when burned. Burning fossil fuels also releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which contributes to global warming. Global warming is changing ecosystems. The oceans are getting warmer and more acidic, threatening marine life. Sea levels are rising, posing a threat to coastal residents. Many areas are more affected by droughts, while others are affected by floods.
Scientists are exploring alternatives to fossil fuels. They are trying to produce renewable biofuels for cars and trucks. They want to produce electricity using the sun, wind, water and geothermal energy – the earth’s natural heat.
Everyone can help save fossil fuels by using them carefully. Turn off lights and other electronics when not in use. Buy energy-saving appliances and protect your home from bad weather. Walk, ride a bike, use public transport whenever possible.
Minerals
Mineral reserves on Earth are under threat. Many of the mineral deposits that have been discovered and mapped have been depleted. As ores for minerals such as aluminum and iron become increasingly difficult to find and mine, their prices skyrocket. This makes tools and equipment more expensive to buy and operate.
Many mining methods devastate the environment, destroying the soil, plants and habitats of various animal species. They also pollute water and air as toxic chemicals enter the surrounding ecosystem.
Less wasteful mining methods and recycling of materials will help conserve mineral resources.
Electronic devices present a big problem for conservation because technology changes very quickly. For example, consumers typically change their cell phones every 18 months. Computers, televisions and mp3 players are other products that cause people to generate even more e-waste. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimated that in 2007, Americans produced over 3 million tons of e-waste.
Electronic products contain minerals as well as petroleum-based plastics. Many of them also contain hazardous materials that can enter soil and water supplies from landfills.
Many governments pass laws requiring manufacturers to recycle used electronics.Recycling not only prevents materials from ending up in landfills, but it also reduces energy consumption for the production of new products. For example, aluminum recycling saves 90 percent of the energy that would be required to extract new aluminum.
Forest natural resources
Trees provide habitat for birds, insects, and other animals, and are essential for the production of oxygen, which is vital to life on Earth. In addition, forest natural resources are used in the production of important products such as timber, paper, fruits and nuts.
Trees are the livelihoods of more than 1.5 billion people around the world – about 20 percent of the world’s population – depend on trees, and our goal is to conserve them as much as possible.
Every year, the Earth loses about 14.6 million hectares of forest due to deforestation. Deforestation destroys wildlife habitats and increases soil erosion. It also releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. Deforestation accounts for 15 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions. Deforestation also hurts people who rely on forests for their survival, hunting and gathering, harvesting forest products, or using wood for firewood.
Water resources
Water is a renewable resource. However, most of the water on the planet is not available for human use. While over 70 percent of the Earth’s surface is covered with water, only 2.5 percent is fresh water. Of this fresh water, almost 70 percent is permanently frozen in the ice caps that cover Antarctica and Greenland.Only about 1 percent of the fresh water on Earth is available to humans for drinking, bathing and irrigating crops.
People in many parts of the world suffer from water scarcity. This is caused by depletion of groundwater sources known as aquifers, lack of rainfall due to drought, or pollution of water sources.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 2.6 billion people do not have adequate sanitation for their water supply. More than 5 million people die each year from diseases caused by using contaminated water for drinking, cooking or washing.
About a third of the world’s population lives in areas experiencing water shortages. Most of these areas are in developing countries.
Polluted water harms not only people but also the environment. For example, agricultural runoff—water that runs off farmland—may contain fertilizers and pesticides. When this water enters streams, rivers and oceans, its use can harm the organisms that live in or drink from these water sources.
People can conserve and conserve water in a variety of ways by limiting their water use, fixing leaky faucets, showering faster, planting drought-tolerant plants, and purchasing appliances that consume less water. Governments, businesses and non-profit organizations can help developing countries build sanitation facilities.
Types of natural resources
Natural resources are derived from the environment. Some resources are necessary for survival, while others simply meet the needs of society. Every product created by man, to one degree or another, consists of certain types of natural resources.
There are many ways to classify the types of natural resources, they include the source of origin, the state of development and the renewable nature of the resources.
According to the source of origin, natural resources can be divided into the following types:
Biotic species
these resources come from living and organic materials, such as forests and animals, and include the materials that can be obtained from them. Biotic natural resources also include fossil fuels such as coal and oil, which are formed from decomposed organic matter.
Abiotic species
these resources come from non-living and inorganic material. Examples of these resources include land, fresh water, air, and heavy metals (gold, iron, copper, silver, etc.).
Natural resources can also be classified according to their stage of development, including:
Potential resources
it is the kind of resources that exist in the region and can be used in the future. For example, if a country has sedimentary oil, it is a potential resource until it is extracted from the rock and used.
Actual resources
it is the kind of resources that have been surveyed, their quantity and quality determined, and they are currently being used. The development of the actual resources depends on the technology.
Reserve resources
it is a piece of a real resource that can be cost-effectively developed in the future.
Stock resources
these are resources that have been surveyed but cannot be used due to lack of technology. An example of a reserve resource is hydrogen.
Natural resources are also classified according to their renewability:
Renewable type of natural resources
These are resources that can be replenished. Examples of renewable resources include sunlight, air and wind. They are available all the time, and their quantity does not depend on human consumption. However, renewable resources do not have a fast recovery rate and are subject to depletion if overused.
Non-renewable type of natural resource
these resources form very slowly and do not form naturally in the environment. A resource is considered non-renewable when its rate of consumption exceeds the rate of recovery. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of non-renewable natural resources.
Exhaustible and inexhaustible natural resources
The classification of types of natural resources depends on their exhaustibility and restorative capacity.
Inexhaustible resources can be updated over time. These include living resources such as forests or non-living resources such as wind, water, solar energy. Renewable resources can be replenished at about the same rate they are being used. Renewable resources, however, can be depleted if they are not used properly.
Exhaustible resources, as the name suggests, are those that can no longer be used once the available supply at the facility is depleted. Once we use them, they will no longer exist. Fossil fuels are considered non-renewable. Non-renewable resources are depleted faster than they can be replenished. Fuels such as oil and natural gas have been formed over millions of years. Once mined and fully utilized, non-renewable resources disappear forever.
Fossil fuels currently account for about 90 percent of the world’s energy consumption. Fossil fuel consumption is almost doubling about every 20 years, which is a rather alarming statistic given that their levels are dangerously low.
Natural economic resources
Natural resources, both renewable and non-renewable, are part of the true wealth of nations. They represent natural capital from which other forms of capital are formed.
They help increase tax revenues, incomes and reduce poverty.Natural resource industries provide jobs and often livelihoods in poorer communities.
Because of this fundamental importance of natural resources, they need to be managed sustainably. Government plays a critical role in implementing policies that ensure that resources contribute to the long-term economic development of nations, and not just the short-term income of one generation.
Natural conditions and resources
Natural conditions for the distribution and use of resources around the world are not the same, and some people have better access to resources than others. Those. different regions have different access to different renewable or non-renewable natural resources, such as fresh water, fossil fuels, fertile soil or timber, depending on their geographic location and past geological processes.
Access, or lack thereof, contributes to the economic development of the place, political relations and culture.
Some regions may have fertile soils or an abundance of vegetation, while others may have an abundance of gems. This uneven distribution led to trade. In one area, you can buy a scarce resource that is available in abundance somewhere else. Sometimes the location of resources is in conflict because one side is trying to take over a given resource that is already under the control of someone else.
Natural resources are unevenly distributed around the world. Some places are more prosperous than others – for example, some regions have a lot of water (and access to the ocean and seas).Others have many minerals and forest areas. Others have metal rocks, wildlife, fossil fuels, and so on.
For example: The spread of fertile soil is a determining factor for agriculture. The world’s best soils are found in southern Russia, the South American pampas, and the American Prairies in the United States. There is intensive agricultural activity in these regions. Regions of Southeast Asia, southern China, South America and sub-Saharan Africa also have productive soils.
Huge oil reserves are stored in the Middle East, especially in Saudi Arabia, Iraq and Iran. Venezuela in South America also stores it in huge quantities. In the United States, most of the oil and gas is located in Texas and along the Gulf Coast.
Russia has the largest reserves of natural gas and is also the largest producer. Iran and Qatar have plenty of gas, but the United States is the second largest producer (albeit with only one-fifth of Russia’s).
Countries rich in precious metals include Australia and South Africa, where diamonds are plentiful. China, Russia, USA, Canada and Peru are the largest gold producers.
Fresh water is becoming more and more valuable. The Amazon Basin, especially Brazil and Colombia, has the most fresh water, followed by North America. On the other hand, Russia and China also have large reserves.
There are many other natural resources, and they are unevenly distributed, with the result that some countries become large producers while others depend on imports.
Use of natural resources
 Overexploitation of natural resources harms the health of ecosystems and the well-being of people.
Overexploitation of natural resources harms the health of ecosystems and the well-being of people.
All types of natural resources play a key role in human well-being. People cannot live without clean air to breathe, plants to eat or water to drink. Natural resources are needed to build a roof over our heads and heat our homes. They are essential for survival and prosperity.
Nature makes human development possible, but our relentless need for the earth’s resources is accelerating the rate of extinction and destroying the world’s ecosystems. The amount of materials used in production and consumption continues to grow globally, and the rate of extraction of materials around the world is outpacing both population growth and economic growth, which means we are using more materials and less efficiently.
If this process continues, global resource extraction will increase by 110% by 2060.
The earth’s natural resources, including air, water, land, flora and fauna, must be conserved for the benefit of present and future generations through careful planning or management, as appropriate. The land’s ability to produce vital renewable natural resources must be maintained and, where possible, restored or improved.
The non-renewable resources of the earth must be used in such a way as to protect against the danger of their depletion in the future and so that the benefits from such use are shared among all mankind.
Problems of the environment and natural resources
People often waste natural resources. Animals are over-hunted. Forests are cut down, exposing the land to wind and water. Fertile soil is depleted and lost due to erosion and inefficient agricultural practices. Fuel reserves are exhausted. Water and air are polluted.
If resources are carelessly managed, many of them will be used up forever. However, if used wisely and efficiently, renewable resources will last longer. People can reduce waste and manage natural resources wisely.
Over the past two centuries, the human population has grown tremendously. Billions of people use up resources quickly when they eat food, build houses, produce goods, and burn fuel for transportation and electricity. The continuation of life as we know it depends on the careful use of all kinds of natural resources.
Extraction, processing and use of natural resources cause environmental problems such as air, land and water pollution; disruption or destruction of ecosystems; and biodiversity loss. For example, carbon dioxide, which is produced from burning coal, oil, and natural gas (fossil fuels), is a greenhouse gas.Greenhouse gases absorb and retain heat from the sun. The formation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can cause global climate change.
The extraction and use of natural resources can also disrupt relationships within ecosystems. For example, cutting down trees destroys the habitats used by many animals, forcing them to look for homes elsewhere. If animals leave their habitats, further disturbances will occur in plant and animal populations that depend on these species.
Conservation of natural resources
People can do a lot to help conserve resources. Turning off lights, repairing leaky faucets, and recycling paper, aluminum cans, glass, and plastic are just a few examples. Cycling, walking, car sharing and using public transportation help save fuel and reduce the amount of pollutants released into the environment. People can plant trees to create homes for birds and squirrels. Bring your own reusable shopping bags to grocery stores. Use reusable water bottles and coffee mugs rather than disposable containers.
If each of us would contribute to conservation a little, the overall result would be serious.
Human needs must be met, but the environment and natural resources must be preserved.
P.S.
If you liked and found this information useful, please share it on social media. networks with your friends and acquaintances. This is how you support our project “Ecology of Life” and make your contribution to the preservation of the environment!
- Magnetic storms: the sun is testing the planet🌪️ - 13.06.2024
- Why You Should Drink Chicory: Benefits and Harms 🌿 - 09.06.2024
- Innovative Choice: Sproud Milk – Your Ideal Plant-Based Drink 🌱 - 03.06.2024