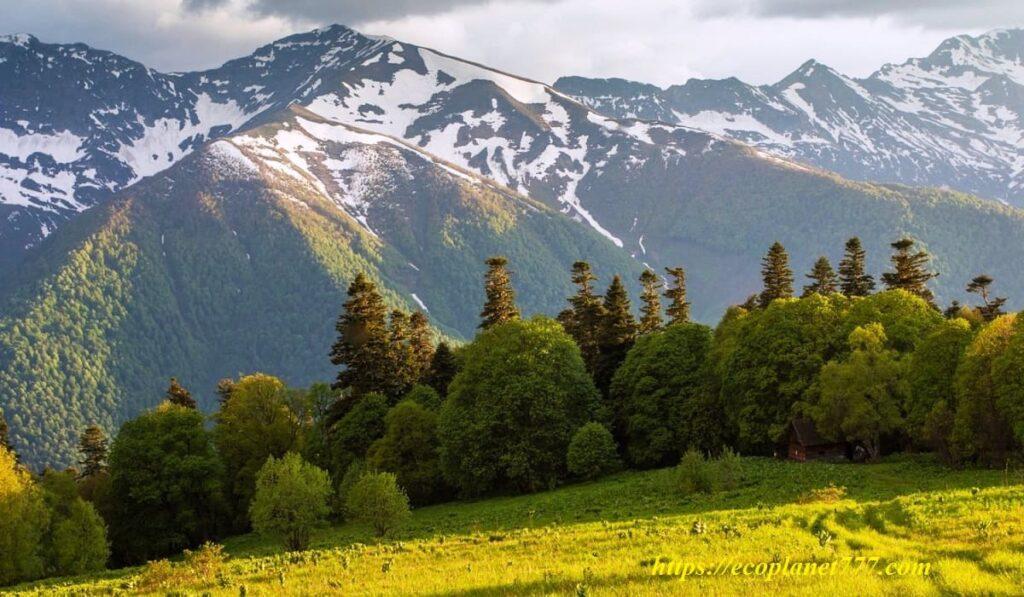
To address issues related to the conservation of biodiversity, a natural biosphere reserve has been created. These unique areas provide a special environment for both people and nature and are living examples of how people and nature can coexist while respecting each other’s needs.
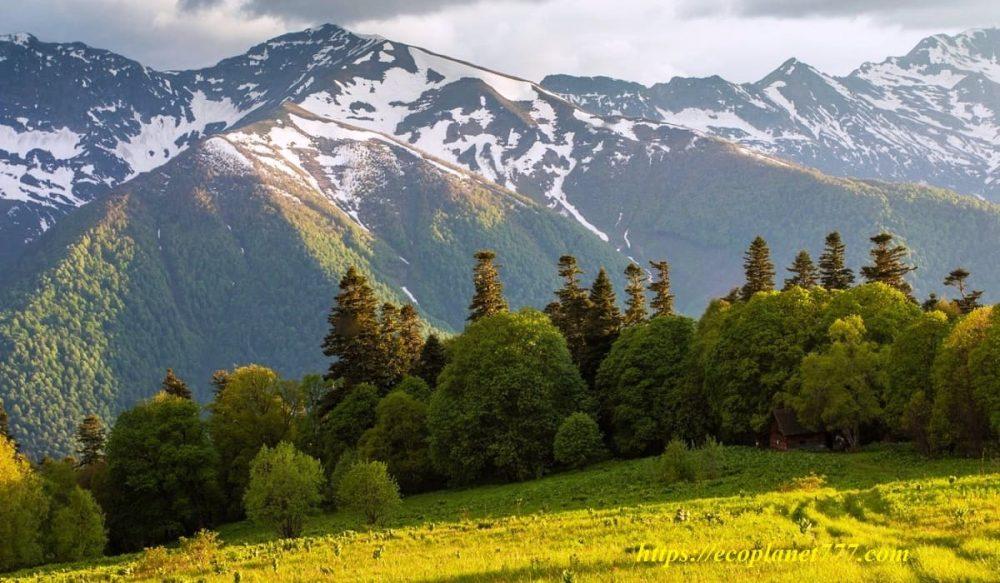

Biosphere reserves are “places of learning for sustainable development”.
Criteria for the designation of a biosphere reserve
A site that must contain an effectively protected and minimally disturbed core area of conservation value.
Structure of the biosphere reserve
Biosphere reserves are divided into 3 interconnected zones:
Main zone
The core zone should contain suitable habitat for numerous plant and animal species, including higher order predators. The core area is a national park or nature reserve and is protected (regulated) primarily under the Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972. This area must be free from human pressure external to the system.
Buffer zone
The buffer zone adjoins or surrounds the main zone. The use and activities in this zone are managed in a way that helps protect the main zone in its natural state. These uses and activities include restoration, demonstration sites to add value to resources, limited recreation, tourism, fishing, grazing, etc.; who are allowed to reduce its impact on the main zone. Research and educational activities should be encouraged.Human activities, if they are natural within the buffer zone, are likely to continue if they do not adversely affect ecological diversity.
Transition zone
The transition zone is the most remote part of the biosphere reserve. It is generally an unrestricted area of cooperation in which conservation knowledge and management skills are applied and the use is managed in accordance with the purpose of the biosphere reserve. This includes human settlements, agricultural land, managed forests and intensive recreation areas, as well as other characteristics of the region’s economic use.
Biosphere reserves are designated by national governments and remain under the sovereign jurisdiction of the states in which they are located. Biosphere reserves are defined within the framework of the MAB intergovernmental program by the Director-General of UNESCO in accordance with the decisions of the MAB International Coordinating Council (MAB ICC). Their status is recognized worldwide.
Functions of biosphere reserves
Biosphere reserves involve local communities and all stakeholders in planning and management.
They combine three main functions:
- Conservation of biodiversity and cultural diversity.
- Economic development that is socio-cultural and environmentally sustainable.
- Logistic support, development support through research, monitoring, education and training.
These three functions are performed by the three main zones of biosphere reserves.
The World Network of Biosphere Reserves covers an area of 6,812,000 km2 in 129 countries. It’s almost the size of Australia.
About 257 million people live in biosphere reserves around the world.
P.S.
If you liked and found this information useful, please share it on social media. networks with your friends and acquaintances. This is how you support our project “Ecology of Life” and make your contribution to the preservation of the environment!
- Magnetic storms: the sun is testing the planet🌪️ - 13.06.2024
- Why You Should Drink Chicory: Benefits and Harms 🌿 - 09.06.2024
- Innovative Choice: Sproud Milk – Your Ideal Plant-Based Drink 🌱 - 03.06.2024